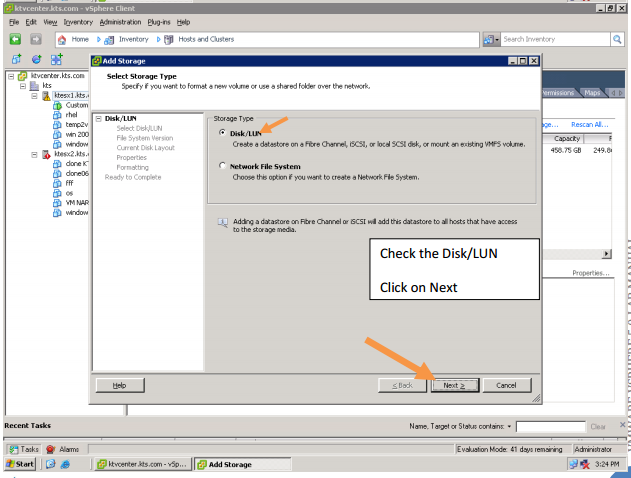
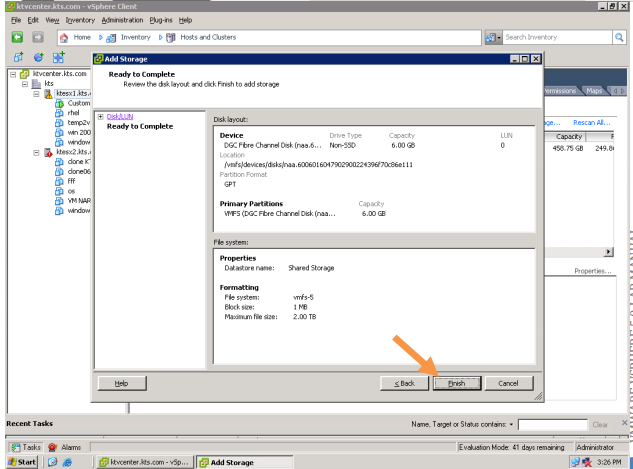
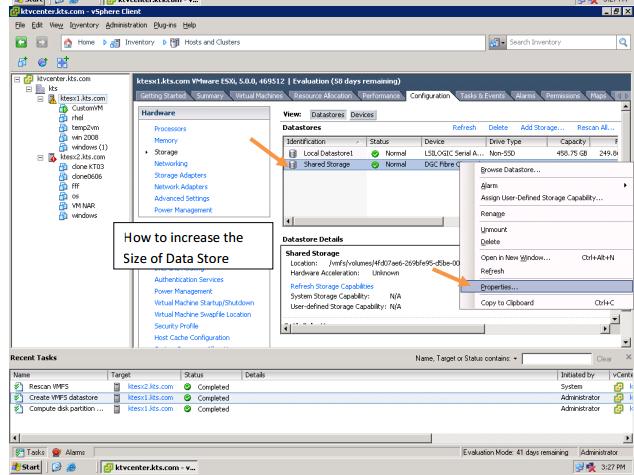
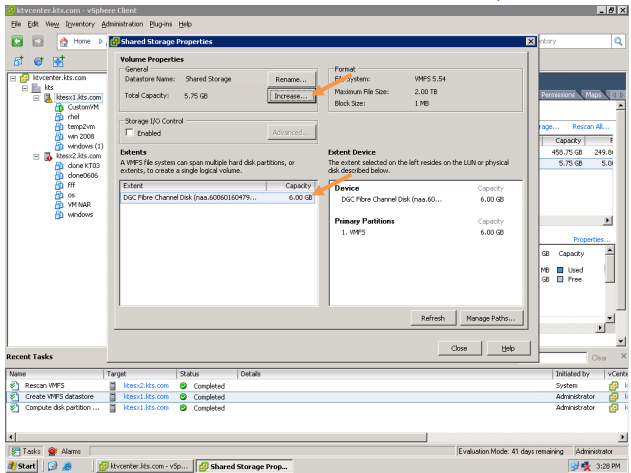
In enterprises, the data is stored on a separate storage device.
The DAS, NAS, and the SAN technologies implemented to store the data. Let us briefly understand DAS, NAS and SAN.
The different Storage technologies are :
-DAS.
-Fiber channel.
-Fiber channel over Ethernet.
-Network Area Storage
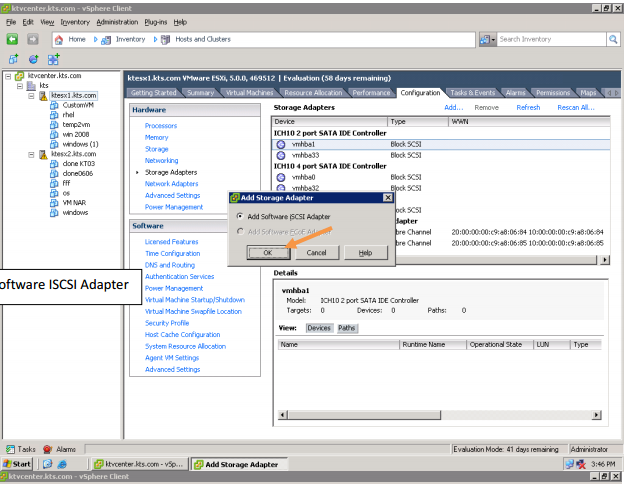
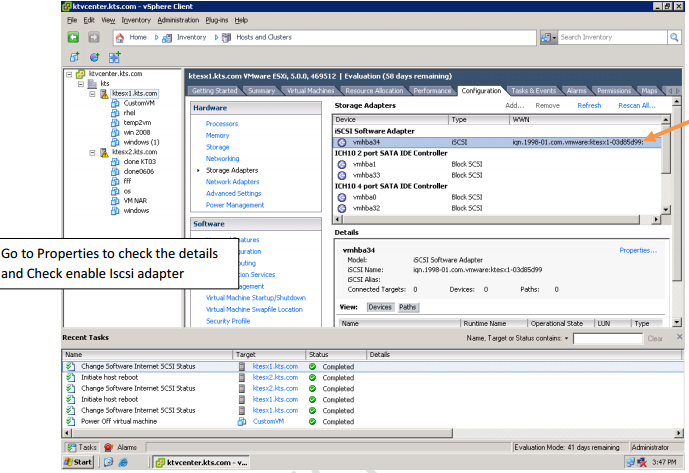
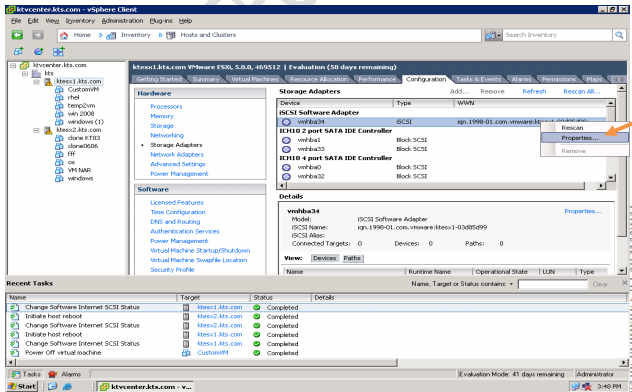
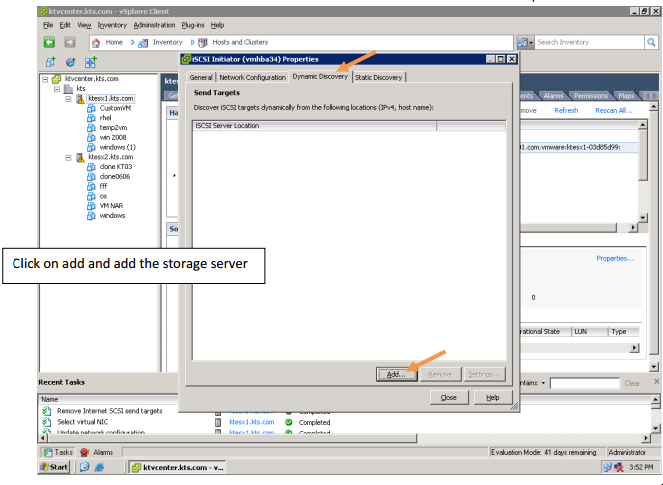
-ISCSI.
DAS: Direct Attached Storage. Storage (usually a disk or tape) is directly attached by a cable to the computer processor. (The hard drive inside a PC or a tape drive attached to a single server is simply a type of DAS.) I/O requests (also called protocols or commands) access devices directly.
Example: ESX1, ESX2 servers in the data center of Kernel Technologies
Learn VMware by Tekslate - Fastest growing sector in the industry. Explore Online "VMware Training" and course is aligned with industry needs & developed by industry veterans. Tekslate will turn you into Pentaho Expert.
SAN: Storage Area Network. Storage resides on a dedicated network. Like DAS, I/O requests access devices directly. Today, most SANs use Fiber Channel media, providing an any-to-any connection for processors and storage on that network. Ethernet media using an I/O protocol called iSCSI is promising.
Example: the EMC storage in the data center of Kernel Technologies
NAS: Network Attached Storage. A NAS device (“appliance”), usually an integrated processor plus disk storage, is attached to a TCP/IP-based network (LAN or WAN) and accessed using specialized file access/file sharing protocols. File requests received by a NAS are translated by the internal processor to devise requests.
Example: the NetApp storage in the data center of Kernel Technologies The term host bus adapter (HBA) is most often used to refer to a Fibre Channel interface card; each HBA has a unique World Wide Name (WWN), which is similar to an Ethernet MAC address. The major Fibre Channel HBA manufacturers are QLogic and Emulex. HBA is also known to be interpreted as a High Bandwidth Adapter in cases of Fibre Channel controllers.
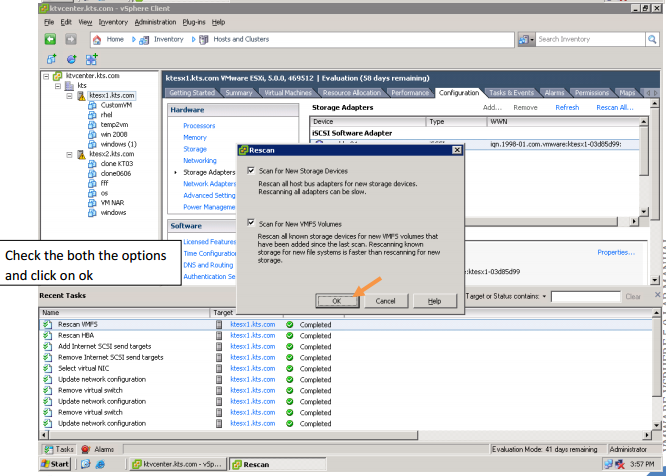
Storage Policy is Fixed (Fixed), Most Recently Used (MRU), Round Robin (RR).
Most Recently Used (MRU) — Selects the first working path, discovered at system boot time. If this path becomes unavailable, the ESX/ESXi host switches to an alternative path and continues to use the new path while it is available. This is the default policy for Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs) presented from an Active/Passive array. ESX/ESXi does not return to the previous path when if, or when, it returns; it remains on the working path until it, for any reason, fails.
Fixed (Fixed) — Uses the designated preferred path flag, if it has been configured. Otherwise, it uses the first working path discovered at system boot time. If the ESX/ESXi host cannot use the preferred path or it becomes unavailable, ESX/ESXi selects an alternative available path. The host automatically returns to the previously-defined preferred path as soon as it becomes available again. This is the default policy for LUNs presented from an Active/Active storage array.
Round Robin (RR) — Uses an automatic path selection rotating through all available paths, enabling the distribution of load across the configured paths For Active/Active storage arrays, all paths will be used in the Round Robin policy. For Active/Passive storage arrays, only the paths to the active controller will be used in the Round Robin policy.
Notes: Round Robin is not supported on all storage arrays. We need to check with the array documentation or storage vendor to see if Round Robin is supported and/or recommended for the array and configuration. Switching to an unsupported or undesirable pathing policy can result in connectivity issues to the LUNs (worst case if can cause an outage).









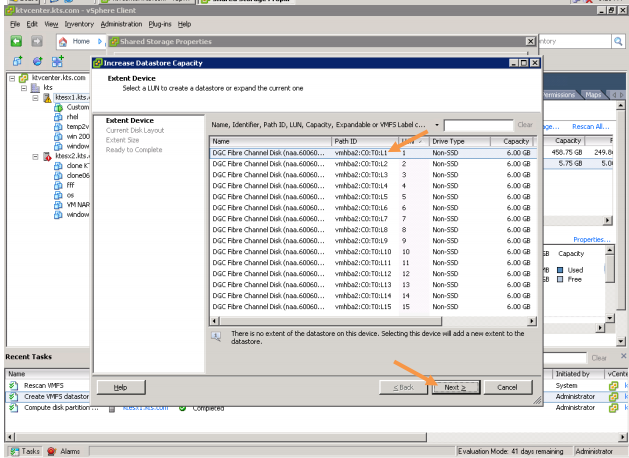





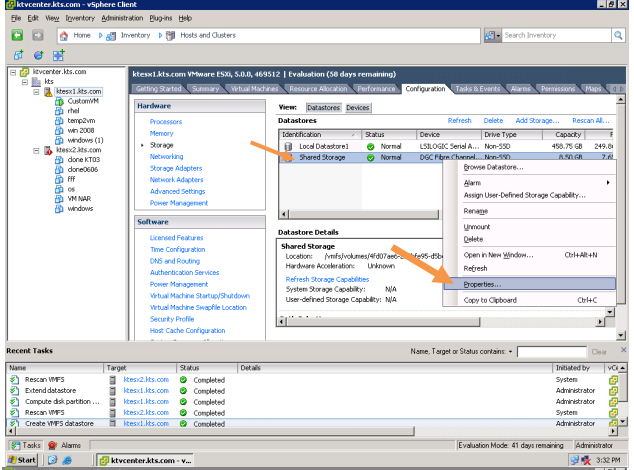
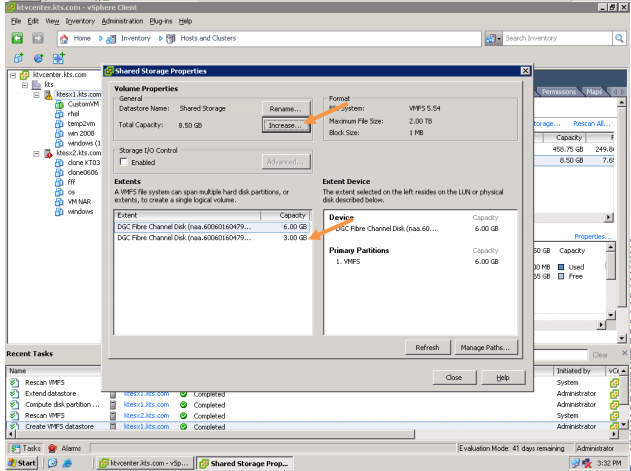



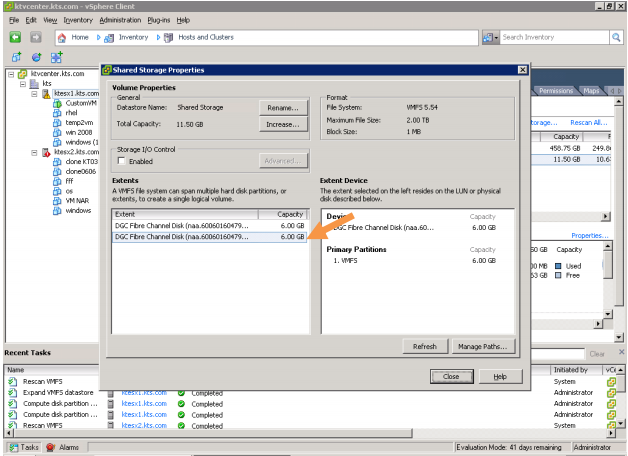













You liked the article?
Like: 0
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty (Avg): Medium

TekSlate is the best online training provider in delivering world-class IT skills to individuals and corporates from all parts of the globe. We are proven experts in accumulating every need of an IT skills upgrade aspirant and have delivered excellent services. We aim to bring you all the essentials to learn and master new technologies in the market with our articles, blogs, and videos. Build your career success with us, enhancing most in-demand skills in the market.