PE BYNET AMP VSS 5.V DISK
AMP is vproc. vproc is nothing But a collection of instructions, which performs a specific operation(or)Task
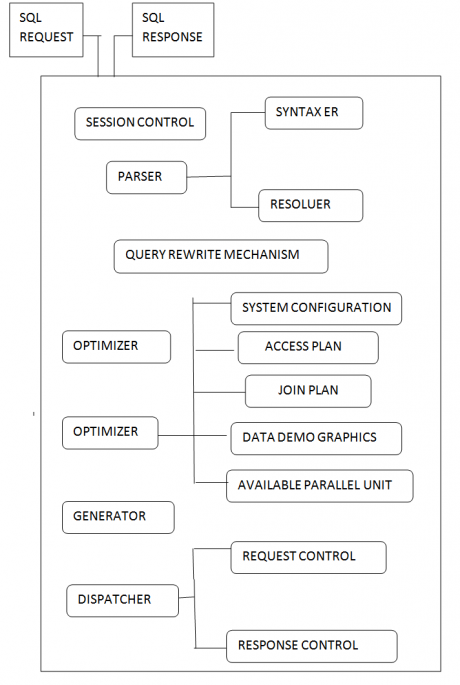
It takes SQL Request and delivery SQL response
Inclined to build a profession as Teradata Developer? Then here is the blog post on, explore Teradata Training
It writes the Query such away optimizer can understand easily
Example:
IF The Query is Q7, it converts into Q2
It is an important component in any database including Teradata It provides an execution plan for SQL Statement so that it is going to be executed by the database Generally it usages the below information.
It generated steps for the plan provided
It performs and manager request and response, flow control(Taking Request, Response keeping in Queue in delivery)
Note:
Passing Engine Handle max 120 sessions at a time
It acts as a” Message communication layer” between various components.
POINT - POINT-One message from PE To one AMP
MULTI CAST-One message from PE to Many AMPs
BROAD CAST- One message from PE to All AMPs
POINT- POINT-One message from One NODE to other NODE
MULTI CAST-One message from One NODE to Many NODE
BROAD CAST- One message from One NODE to All NODE
1. Each AMP is responsible for managing a portion of MAIN DISK SPACE (VIRTUAL DISK)
2. This space not sharable by any other AMPs so we call architecture as shared-nothing architecture.
3. Each AMP Operator independently resources
4. Each AMP contains a database management subsystem. If perform the below operations.
Note:
Max so task AMP TO perform at a time
Multiple AMP runs independently so high parallelism implement
a) AMPS know the physical location of the cylinder which are address by DRIVE# (OR) CYLINDER#
b) Adjusting system AMPS integral number of drives per AMP
c) Adding storage requires an additional drive per AMP.
a) AMPs don’t know the physical location of the cylinder and it can be changed, because of the cylinder in CLIQUE’s On effective in the pool, that are managed by Teradata virtual storage, virtual process.
b) Added drives are shared by all AMP’s
c) You can add several drives, This new Drive may have different capacity are performance than those drives, which are already present in the system

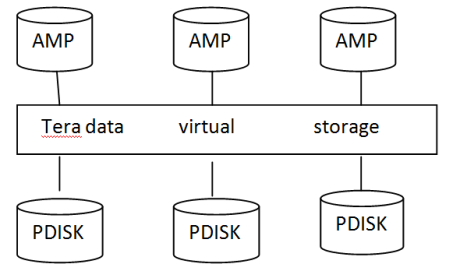

Collection of physical DISK (OR) Group of cylinder Arranged in Array position is called VDISK(or) virtual DISK Traditionally this called as DISK Array (or) Array of DISK After AMP performance operation, it invokes the controller this store and manages the data across physical disk This controller active array controller, the number of cylinders in an Array is called a RANK in the above Diagram the Rank is 3.(N-1)=4-1=3

For connection to the Teradata database system, we need to connect through either CHANNEL ATTACHED SYSTEM OR NETWORK ATTACHED SYSTEM
It just like TDP cannot balances to sessions
It is a low-level interface for request, response Blocking, and un- Blocking.
It checks the platform Independence of the operating system.
You liked the article?
Like: 0
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty (Avg): Medium

TekSlate is the best online training provider in delivering world-class IT skills to individuals and corporates from all parts of the globe. We are proven experts in accumulating every need of an IT skills upgrade aspirant and have delivered excellent services. We aim to bring you all the essentials to learn and master new technologies in the market with our articles, blogs, and videos. Build your career success with us, enhancing most in-demand skills in the market.